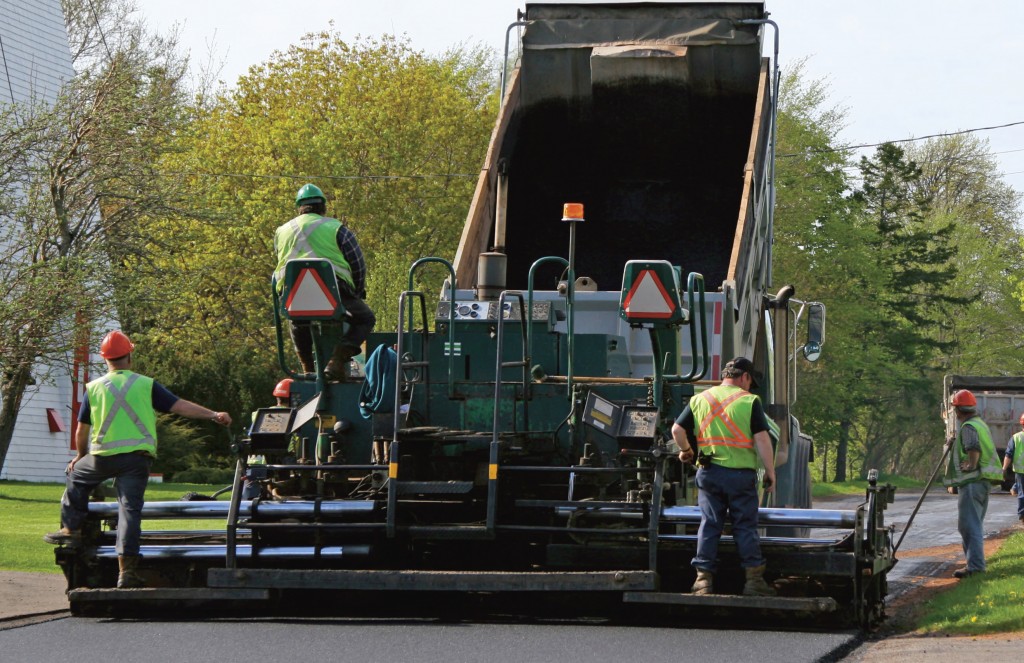
How Can We Make County Roads Last Longer?
County Progress tapped into the know-how of some of the state’s leading road experts headquartered at Texas A&M and the University of Texas at Arlington.
Question: What are the keys to building long-lasting roads?
Answer: Greg Brinkmeyer, P.E., Senior Training Specialist, Local Technical Assistance Program (LTAP), Texas A&M Engineering Extension Service (TEEX), a member of the Texas A&M University System
- Good quality base materials
- Monitored compaction of base materials
- Sufficient crown from the roadway’s center to the edge to ensure drainage of water from the roadway surface
- Adequately sized ditches or drainage structures to handle surface water that drains from the roadway surface and adjacent lands. Water is the biggest enemy of any type of roadway surface.
Answer: Howard McCann. P. E., Bruce Eliker and Eldon McCurley, faculty members, University of Texas at Arlington’s (UTA) Public Works Institute
- Road users expect good, well-maintained roads; it must also be understood that building and maintaining long-lasting roads requires an ongoing funding commitment from the public. It is our experience that the public recognizes that there is no “free lunch” when it comes to paying for good roads, and that the public likewise expects public officials to do the right things, and do the right things well, in order to “get the most bang” out of every dollar of taxpayer money spent.
- Roads are built from the ground up. A good foundational sub-grade, sub-base and base materials with the proper density are required to achieve roads that will support the anticipated vehicle loads and the anticipated traffic volume.
Roadbuilders of an earlier generation saw firsthand how long convoys of World War I Army trucks (trucks far below the capacity of modern trucks) virtually destroyed a section of highway on the East Coast that was previously regarded as a good road; the road simply had not been built to handle the heavy loads of the early trucks. Members of that generation were strong believers and sponsors of the research that continues today that led to the development of today’s well-established geometric and pavement design standards.
- Geometric design features must be taken into account to establish a roadway that provides the best travel while still controlling cost. Geometric design consists of the alignment of the road and the profile of the road, as well as the cross section of the roadway. The cross section shows many items, most importantly the drainage features that are so important.
- Good drainage is crucial. The two main causes of pavement and gravel road surface and support structure failures are WATER & TRAFFIC LOADING. It is important to control water infiltration/intrusion either through the road surface into the base/sub-base or into the base/sub-base and sub-grade from improperly maintained ditches and drainage structures. Always try to keep ditches clear of standing water, and where possible maintain a flow line lower than the base and sub-structure of the roadway. Also, it is very important to properly design any cross-road drainage systems (culverts, bridge structures, etc.) to handle the anticipated water flow.
Question: What are the keys to maintaining long lasting roads?
Answer: Greg Brinkmeyer, P.E., LTAP, TEEX
- Again, water is the biggest enemy to a roadway. Roadway agencies must ensure that water quickly drains from the roadway surface into adjacent ditches or drainage structures. On rural roadways, it is important to “cut” the edge of the roadway to remove dirt and grass that builds up next to the edge of the roadway that impedes the drainage of water from the roadway. As water ponds next to the edge of the roadway, it will slowly seep into the underlying base material. Over time, this causes the pavement edge to ravel and creates pavement edge drop-offs.
- On the pavement surface, fog sealing and crack sealing are important to prevent water from penetrating the underlying base material. Once water penetrates the base material, the roadway surface will quickly deteriorate resulting in rutting and pot holes.
- Restricting and enforcing overweight loads
Answer: Howard McCann. P. E., Bruce Eliker and Eldon McCurley, faculty members, UTA’s Public Works Institute
- Develop a strategic maintenance plan and follow it. Preventative Maintenance (PM) techniques help preserve the investment made by the local road agency. Properly assessing the conditions of your roadways and maintenance needs is paramount. In today’s world we cannot afford to perform the wrong treatment when performing PM. It’s very important to take an inventory of your roadways and assess their condition; this is the only way to determine your maintenance needs and to be able to budget for needed repairs and PM. Remember, good PM keeps the water out of the pavement structure and helps prevent and slow distresses from reoccurring.
- With asphalt pavements, stay away from the “worst-first” approach to solving your roadway maintenance needs. Keeping good roads in good condition is the best PM strategy to follow. It pays to take care of your good roadways and promptly address all minor maintenance needs. With new road surfacing, you may begin to see roads age after about three years or so. When aging is first noticed, preventative maintenance efforts should be initiated to preserve and extend the longevity of the pavement. It pays to “keep good roads good” as they are an expensive investment.
For gravel roads maintenance, it is important to select good surface gravel, no large than ¾” in size, with good fines and plasticity. Along with proper blading and compaction to maintain the road crown, this will promote a long-lasting road surface. In addition, it is important to keep all bar ditches and drainage structures clear.
- PM can never fix a failed sub-structure of a roadway. Failed sub-structures can only be corrected by rehabilitation or reconstruction, the two most expensive maintenance repairs. By staying in the “worst-first” approach to PM, you won’t have the time or money to keep your good roadways from deteriorating and falling into the worst category of maintenance needs.
- The life of a pavement is dependent on routine and preventive maintenance strategies. It is recognized that many counties and other local road agencies do not have a county engineer and have little in the way of technical resources; however, there is a local source that can be of much value to you, and that is the local TxDOT area engineer’s office. These offices have a qualified technical staff and know the local area, and they are aware of the materials and resources available in that area. They can be of much benefit to you, and it’s important to build a good working relationship with them.
Answer: Elton Glidewell, faculty member, UTA’s Public Works Institute
- The problems associated with inadequate drainage compound themselves exponentially. Moisture penetration is one of the major causes of road failure. It leads to potholes, base failures and edge failure. Inadequate drainage, ditches that don’t flow properly, and culverts that are stopped up must be addressed and be corrected as soon as possible. Employ a dedicated drainage crew, if possible, or make a concentrated effort during the winter months when road construction is not an option. This is very important on gravel roads, as they are very susceptible to moisture penetration.
- Crack sealing to prevent moisture penetration is one of the most overlooked aspects of preventative maintenance. It is very cost effective and requires a minimum of skill and equipment. Crack sealing definitely helps prevent moisture penetration, which leads to the softening of the base material, potholes and base failure.
- The immediate repair of potholes and pavement failures to contain any problems is also important. These only get larger and tend to compound themselves with daily traffic and rain or snow conditions. There are several pothole patching machines available. While these are not as good as a permanent repair, if done properly they do seal the failure and help prevent further deterioration.
- Almost any roadway will need a surface seal every five years. I prefer a properly applied chip seal, as this seals the surface and improves skid resistance. However, there are several fog seal or slurry seal applications that work fairly well and eliminate complaints of loose rock and windshield damage. These are less expensive and less time consuming to apply and are very popular in residential areas.
Preventive maintenance is the primary key to having a road that is safe for the driving public. It also protects the investment of the public from extensive depreciation. A new road, if it is not maintained properly, will likely need to be re-constructed in 12 years to 15 years. As an example of preventative maintenance, some of the older highways that were built in the 1930s and have been properly maintained are still in use today, some 80 years later.
Question: How does strategic planning contribute to the success of a road program?
Answer: Greg Brinkmeyer, P.E., LTAP, TEEX
First of all, successful agencies recognize that to be successful, they must have a road program. However, developing and implementing a road program takes a commitment of time and effort. As traffic demands continue to increase and cities/counties become further stressed to maintain the functionality and quality of their roadway system, typically with limited funds, management plans are going to be a necessity. The use of a management plan allows an agency to successfully schedule and correct roadway deficiencies rather than continuously performing repeated Band-Aid maintenance that in the short term may be less expensive, but in the long-term may require complete reconstruction of the roadway.
Answer: Elton Glidewell, UTA’s Public Works Institute
Strategic planning is one of the main keys to a successful road maintenance program. It is necessary for the wise use of funds by any municipality. Texas has an expanding population that is placing excessive demands on our roadways. With higher traffic counts and heavier loads, is necessary to have long-range plans in place to handle the requirements that will be thrown on the public works departments in the future.
Strategic planning also helps with public awareness and perception. These are often key factors in budget hearings and bond sales. It is also very helpful in the allocation of resources and manpower to have the best and safest roads possible, which is the ultimate goal of any municipality.
One of my first supervisors had a poster framed on his office wall. It was very simple. FAIL TO PLAN – PLAN TO FAIL.